From luxury to necessity: The transformation of AI in the workplace
This article was originally published on High Performance Laptops.
The rise of Generative AI
In November 2022, the world was introduced to a game-changer in technology: ChatGPT. Within five days, it captivated over one million users, and today, more than 100 million people rely on Generative AI (GenAI) to streamline their daily tasks. Imagine turning hours of work into mere minutes – this is the power of GenAI, reshaping productivity and efficiency across industries.
Unprecedented productivity gains
Large scale studies on the use of GenAI at work have shown average productivity gains of 24.5%. (MIT study of 444 white-collar employees, MIT & Stanford study of 5,000 customer service employees, AI at Work Is Here. Now Comes the Hard Part (microsoft.com)). Ordinary users have experienced these gains by integrating GenAI into their daily tasks. We’ve observed clients shifting focus from traditional automation solutions with integrated specialised AI, to this quick-win technology. Interestingly, while junior-level employees benefit most from GenAI in mundane tasks, organisational leaders often remain unaware of its widespread use.
Why the shift from traditional automation to Generative AI is significant
The transition from traditional automation to GenAI marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of workplace technology. Traditional automation involves programming machines or software to perform specific, repetitive tasks based on predefined rules and logic. While beneficial in optimising processes, reducing errors, and saving time in routine operations, it has several limitations:
GenAI transforms workplace technology with its ability to understand, generate, and manipulate human-like text based on vast amounts of data. Here’s why the shift is so impactful:
- Broad applicability: Handles diverse functions, from drafting emails and reports to creating content and providing customer support, making it versatile across sectors.
- Ease of use: Accessible to non-technical staff through natural language prompts, broadening its usability.
- Real-time adaptability: Learns from new data and adapts in real-time, effectively handling unstructured data and responding swiftly to changes.
- Increased efficiency and creativity: Automates both repetitive and complex tasks, allowing human workers to focus on higher-value activities, boosting innovation and strategic thinking.
- Scalability and cost efficiency: Scales operations without significant cost increases, leveraging existing infrastructure for various functions, making it cost-effective.
But traditional automation is far from dead... by integrating GenAI with traditional automation, we can process unstructured information, achieve previously impossible results, and widen the scope of what can be automated.
The presence and secrecy of GenAI use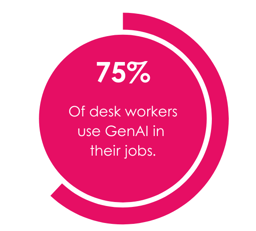
Today, 75% of desk workers use GenAI in their jobs. This statistic often surprises senior leadership teams because users tend to not disclose their use of GenAI, feeling it resembles “cheating” – similar to using a calculator when you’re used to doing long division manually.
Challenges of democratised AI
The democratisation of AI introduces new challenges, particularly in data governance. Leaders increasingly realise that data used in the free AI tools can be used to train the models as seen in the Samsung case.
This realisation has led to various reactions:

The enterprise response
To address these challenges, OpenAI announced an Enterprise version of ChatGPT, offering centralised governance and the assurance that customer data would not be used to train the model. However, the requirement of a minimum of 150 users on an annual commitment puts it out of reach for many organisations.
Enter Microsoft Copilot
Recognising their lag in the GenAI race, Microsoft invested $11 billion in OpenAI to leverage their technology. Microsoft Copilot, a personal assistant embedded in the Microsoft suite of applications, uses the same technology powering ChatGPT. This integration addresses implementation struggles, as user data is not used to train models and there is no 150-user minimum, lowering the barrier to entry.
Challenges in adopting Copilot
Despite its potential, adopting Copilot comes with its own set of challenges:
- Data management: Copilot only accesses information that each user can access, which is great if file permissions are set up correctly. However, it poses a risk of exposing more information than intended. For example, a prompt to summarise knowledge about a colleague might return sensitive documents like salary letters that should not be visible.
- User skills: Effectively prompting Copilot effectively is a new skill that requires learning. Unlike ChatGPT, prompting Copilot to create a presentation from a Word document is less intuitive.
- Product immaturity: While Copilot’s marketing is ahead of its current capabilities, it excels in certain areas. For example, it saves sales teams an average of 20 minutes per meeting by generating Teams meeting draft notes. However, its Excel functionality is basic, making it less suitable for analytical functions like Finance for now.
As the product matures, this limitation will decrease. However, a targeted rollout to relevant teams will return a better ROI than a blanket rollout across the organisation.

How we're helping clients
To support organisations in navigating these challenges, our Copilot accelerator program provides a measured, phased approach to rolling out Copilot. We offer a comprehensive plan that includes target teams, strategic objectives aligned with organisational goals, and risk mitigation plans. As part of this, we train leadership teams to understand and leverage the benefits of GenAI effectively.
In response to surging demand, our training programs have expanded from in-person to online formats, ensuring accessibility and convenience.
Client success stories
Our clients are experiencing significant benefits across various business areas by implementing GenAI solutions. Here are a few use cases:
- Information technology: Streamlined code development, automated documentation, enhanced troubleshooting efficiency, and ensured IT policy compliance.
- Sales and client services: Automated note-taking and follow-up tasks, improved proposal writing, and enhanced client communications.
- Customer service: Improved response times and customer satisfaction through AI-assisted interactions.
- Human resources: Streamlined recruitment processes and enhanced candidate engagement through AI-driven insights.
- Marketing: Boosted SEO with better keyword ideas, enhanced content generation, developed effective strategies, and provided deep market analysis.
The path forward
Generative AI is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern businesses. Its broad applicability, ease of use, real-time adaptability, and cost efficiency make it a powerful tool for boosting productivity and innovation. Organisations not adopting GenAI risk falling behind in efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. By strategically implementing GenAI solutions and investing in user training, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and maximise their potential in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Author
AI is changing the way businesses operate, and as Head of AI & Automation at The Missing Link, I help organisations harness its full potential. With a background in commercial consulting and intelligent automation, I’ve guided companies in streamlining operations, reducing inefficiencies, and embracing AI-driven innovation. Before joining The Missing Link, I led an automation start-up to profitability and have since trained over 2,000 professionals in generative AI, including Microsoft Copilot and ChatGPT. I’ve also authored books on prompt engineering. When I’m not exploring AI’s capabilities, you’ll find me enjoying yoga, golf, or making my daughters laugh.
-png.png?width=961&height=277&name=Shift%20from%20traditional%20automation%20to%20Gen%20AI%20(1)-png.png)
